Understanding IRAS Singapore: What You Need to Know
Understanding IRAS Singapore: What You Need to Know
Outline

The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) is the nation’s central tax authority, responsible for administering tax collection and ensuring compliance with Singapore’s tax laws. As the primary body overseeing tax policies, IRAS plays a vital role in the economic structure of the country by managing taxes, collecting revenue, and providing advice on financial matters. Both businesses and individuals benefit from IRAS’s structured and efficient tax system, which allows for consistent and transparent management of Singapore’s revenue.
IRAS is also critical to Singapore’s global reputation as a business-friendly hub. Its operations directly affect businesses’ strategic financial decisions and their day-to-day operations, ensuring the country remains competitive on the international stage. By overseeing about 70% of the Singapore Government’s operating revenue, IRAS contributes significantly to funding public services and economic growth, which further benefits businesses operating within the country.
A Brief History of IRAS
IRAS’s history can be traced back to 1947, when Singapore’s Income Tax Department was created. In its early years, the department was responsible for processing around 40,000 individual tax returns and 1,000 corporate tax returns. Over its first few years, it collected $33.2 million in revenue, a small but important start for what would become a central entity in Singapore’s taxation system. Over time, the department’s responsibilities expanded as the country grew economically and politically.
In 1960, the Income Tax Department evolved into the Inland Revenue Department (IRD), consolidating various revenue streams under a single administration. This shift helped streamline processes and made tax collection more efficient. Following Singapore’s independence in 1965, further reforms to the Income Tax Act were introduced, with key changes implemented in 1970. This included the creation of more advanced administrative processes and the first appointment of a local Commissioner. By 1992, IRAS was formally established as a statutory board under the Ministry of Finance. This restructuring allowed IRAS greater autonomy and improved its ability to serve both residents and businesses, helping it become the modern, efficient body it is today.
IRAS’s Core Functions and Authority
IRAS’s two core functions are tax collection and tax advisory services to the government. These functions help maintain Singapore’s status as a global financial hub. As the primary body for managing the country’s tax system, IRAS administers a wide range of taxes that provide essential revenue for public services and government programs. These taxes fund everything from infrastructure to education, healthcare, and social programs, ensuring the continued growth and stability of Singapore’s economy.
IRAS also plays a key role in advising the Singapore Government on matters of tax policy and international tax matters. It drafts tax legislation, participates in international tax treaty negotiations, and develops policies that support Singapore’s long-term economic goals. Through its advisory capacity, IRAS helps to shape Singapore’s tax framework to ensure it remains competitive and attractive for both local and international businesses, encouraging investments while providing stability and legal clarity for companies operating in the country.
Tax Collection Role of IRAS
As the nation’s primary tax authority, the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) plays a crucial role in the administration of Singapore’s tax system. It is responsible for collecting a broad range of taxes, which are essential to funding the country’s public revenue. These taxes support various sectors, including government initiatives, social services, and economic infrastructure projects. Some of the key taxes IRAS oversees include Income Tax for both individuals and businesses, the Goods and Services Tax (GST), Stamp Duty on property and shares, Property Tax, Withholding Tax, and Estate Duty, among others. IRAS also manages taxes related to lotteries, casinos, and clubs, further reflecting the breadth of its responsibilities.
IRAS’s primary function in tax collection ensures that businesses and individuals meet their tax obligations on time and in full. The efficient collection of taxes is crucial for Singapore’s public sector, providing the government with the necessary funds to drive national programs, public services, and infrastructure development. The taxes collected by IRAS fuel critical areas such as healthcare, education, public housing, and defense, contributing to the well-being and security of citizens. Additionally, tax revenues support Singapore’s continued economic growth, enabling the government to invest in innovation, sustainability, and future economic resilience. With a transparent and efficient tax collection system, IRAS ensures that Singapore remains an attractive and stable environment for businesses and investors.
How Does IRAS Manage Tax Collection?
The way IRAS manages tax collection is a key part of Singapore’s reputation as a global business hub. By maintaining an efficient and transparent tax administration, IRAS fosters a reliable and predictable tax environment. Businesses can operate with confidence, knowing that Singapore’s tax system is fair, consistent, and aligned with international best practices. This stability attracts global businesses and investors, encouraging them to base their operations in Singapore. Furthermore, the revenue generated by IRAS supports ongoing investments in infrastructure and public services, which in turn strengthens the nation’s competitive edge on the global stage. As a result, IRAS’s tax collection efforts not only fund public services but also contribute to maintaining Singapore’s status as one of the most competitive and innovative economies in the world.
In addition to its core tax functions, IRAS plays a strategic role in shaping tax policy, providing advisory services to the government, and ensuring that Singapore remains compliant with international tax standards. The taxes collected by IRAS are critical not only for sustaining public services but also for maintaining the high standard of living enjoyed by Singapore’s residents. By effectively managing these revenue streams, IRAS helps position Singapore as an attractive destination for businesses, entrepreneurs, and investors from around the globe.
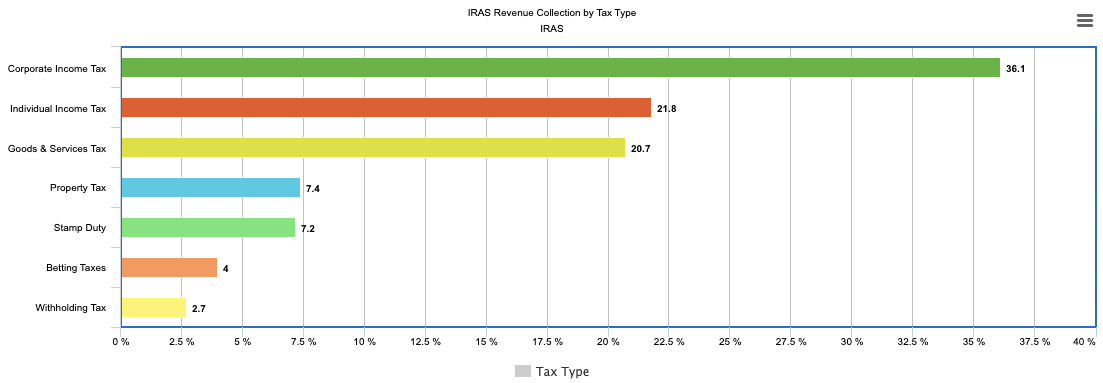
Breakdown of Tax Revenue Collection
The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) plays a crucial role in sustaining the country’s financial stability through its efficient tax collection systems. In the fiscal year 2023/24, Singapore saw a significant increase in tax revenue, driven by strong economic activity and higher consumer spending. The following breakdown provides a detailed overview of the contributions from various tax types to IRAS’s total revenue collection, highlighting the key factors influencing growth in corporate and individual taxes, as well as the impact of consumer behavior and property transactions.
Tax Exemptions and Territorial Taxation
One of the distinguishing features of Singapore’s tax system is its exemption of certain types of income. Unlike many other countries, dividends, capital gains, and inheritance are not subject to taxation in Singapore. This is an attractive feature for both businesses and high-net-worth individuals, as it allows for tax efficiency and wealth preservation. This tax exemption policy enhances Singapore’s position as a global financial center and makes it a favorable jurisdiction for international businesses and investors.
Additionally, Singapore adopts a territorial taxation system, which means that only income sourced within Singapore is subject to tax. If a company or individual generates income outside of Singapore, and that income is not brought into the country, it is generally not taxed by IRAS. This approach encourages businesses to establish operations in Singapore, knowing they will not be taxed on their foreign-earned income. It also facilitates international business and trade by reducing the overall tax burden for companies that operate in multiple jurisdictions.
The Advisory Role of IRAS
In addition to tax collection, IRAS also serves an advisory role in the development and administration of Singapore’s tax policies. It works closely with the Ministry of Finance to craft tax policies and legislation that support the country’s economic goals. This advisory function ensures that Singapore’s tax laws are competitive, fair, and conducive to business growth. It is a key aspect of IRAS’s work, as it helps the government shape policies that attract foreign investment, promote innovation, and ensure long-term economic stability.
One of the most significant aspects of IRAS’s advisory role is its work on Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs). Singapore has signed over 100 DTAs with countries around the world, preventing businesses and individuals from being taxed twice on the same income. These agreements are particularly beneficial for companies with international operations, as they help streamline tax obligations and reduce the tax burden on cross-border income. DTAs are a cornerstone of Singapore’s business-friendly tax regime and are essential for facilitating international trade and investment.
IRAS Filing Calendar 2025
To ensure businesses and individuals meet their tax obligations, IRAS provides a detailed Filing Calendar each year. This calendar outlines key filing deadlines for various taxes, including income tax, GST, and property tax. Adhering to these deadlines is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. The filing calendar helps businesses stay organized and ensures that their tax filings are submitted in a timely manner.
For 2025, some of the key filing deadlines include:
- 31 January: Property Tax Bill for 2025
- 1 March: Employment Income e-Submission
- 31 March: ECI Filing for companies with a December year-end
- 31 May: FATCA and CRS Returns
- 31 October: GST Return for the September period
- 31 December: Corporate Income Tax Returns (Form C-S, Form C-S (Lite))
By staying informed about these important deadlines, businesses can avoid unnecessary fines and ensure their tax matters are handled smoothly.
IRAS’s Digital Integration and Compliance Tools
Business Access
IRAS offers various digital tools to simplify the process of tax filing and compliance for businesses and individuals. The myTax Portal is the central platform for managing tax affairs. Businesses use CorpPass to sign in to the portal, which allows them to submit their tax returns, check their tax status, and manage payments and refunds online. The platform is user-friendly and designed to streamline tax processes, reducing administrative burdens for businesses.
Individual Access
For individuals, SingPass provides secure access to the myTax Portal. The system ensures that personal tax matters are handled confidentially and efficiently. Additionally, IRAS allows businesses to integrate approved accounting software with the myTax Portal, ensuring that data flows seamlessly between financial systems and the tax authority.
Best Practices for IRAS Compliance
To maintain good standing with IRAS and ensure smooth operations, businesses should follow several best practices for compliance:
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keep detailed and organized records of all business transactions, including sales, purchases, and expenses. Accurate record-keeping ensures that your tax returns reflect the true financial position of the company.
- File on Time: Always meet filing deadlines to avoid penalties. Late submissions incur fines, and repeated delays can result in more severe consequences.
- Leverage Digital Tools: Use the myTax Portal and approved accounting software to streamline tax filings and reduce errors.
- Engage Professional Support: Work with corporate service providers like Corpzzy, who specialize in managing tax matters and ensuring compliance with IRAS regulations.
IRAS Digital Assistance: IRAS Bot
For quick guidance and answers to common tax-related questions, businesses and individuals can use the IRAS Bot, an automated virtual assistant available on the IRAS website. The IRAS Bot is a helpful tool for addressing basic queries, allowing users to resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Questions? We Have Answers
About The Author
Related Business Articles
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!


The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) is the nation’s central tax authority, responsible for administering tax collection and ensuring compliance with Singapore’s tax laws. As the primary body overseeing tax policies, IRAS plays a vital role in the economic structure of the country by managing taxes, collecting revenue, and providing advice on financial matters. Both businesses and individuals benefit from IRAS’s structured and efficient tax system, which allows for consistent and transparent management of Singapore’s revenue.
IRAS is also critical to Singapore’s global reputation as a business-friendly hub. Its operations directly affect businesses’ strategic financial decisions and their day-to-day operations, ensuring the country remains competitive on the international stage. By overseeing about 70% of the Singapore Government’s operating revenue, IRAS contributes significantly to funding public services and economic growth, which further benefits businesses operating within the country.
A Brief History of IRAS
IRAS’s history can be traced back to 1947, when Singapore’s Income Tax Department was created. In its early years, the department was responsible for processing around 40,000 individual tax returns and 1,000 corporate tax returns. Over its first few years, it collected $33.2 million in revenue, a small but important start for what would become a central entity in Singapore’s taxation system. Over time, the department’s responsibilities expanded as the country grew economically and politically.
In 1960, the Income Tax Department evolved into the Inland Revenue Department (IRD), consolidating various revenue streams under a single administration. This shift helped streamline processes and made tax collection more efficient. Following Singapore’s independence in 1965, further reforms to the Income Tax Act were introduced, with key changes implemented in 1970. This included the creation of more advanced administrative processes and the first appointment of a local Commissioner. By 1992, IRAS was formally established as a statutory board under the Ministry of Finance. This restructuring allowed IRAS greater autonomy and improved its ability to serve both residents and businesses, helping it become the modern, efficient body it is today.
IRAS’s Core Functions and Authority
IRAS’s two core functions are tax collection and tax advisory services to the government. These functions help maintain Singapore’s status as a global financial hub. As the primary body for managing the country’s tax system, IRAS administers a wide range of taxes that provide essential revenue for public services and government programs. These taxes fund everything from infrastructure to education, healthcare, and social programs, ensuring the continued growth and stability of Singapore’s economy.
IRAS also plays a key role in advising the Singapore Government on matters of tax policy and international tax matters. It drafts tax legislation, participates in international tax treaty negotiations, and develops policies that support Singapore’s long-term economic goals. Through its advisory capacity, IRAS helps to shape Singapore’s tax framework to ensure it remains competitive and attractive for both local and international businesses, encouraging investments while providing stability and legal clarity for companies operating in the country.
Tax Collection Role of IRAS
As the nation’s primary tax authority, the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) plays a crucial role in the administration of Singapore’s tax system. It is responsible for collecting a broad range of taxes, which are essential to funding the country’s public revenue. These taxes support various sectors, including government initiatives, social services, and economic infrastructure projects. Some of the key taxes IRAS oversees include Income Tax for both individuals and businesses, the Goods and Services Tax (GST), Stamp Duty on property and shares, Property Tax, Withholding Tax, and Estate Duty, among others. IRAS also manages taxes related to lotteries, casinos, and clubs, further reflecting the breadth of its responsibilities.
IRAS’s primary function in tax collection ensures that businesses and individuals meet their tax obligations on time and in full. The efficient collection of taxes is crucial for Singapore’s public sector, providing the government with the necessary funds to drive national programs, public services, and infrastructure development. The taxes collected by IRAS fuel critical areas such as healthcare, education, public housing, and defense, contributing to the well-being and security of citizens. Additionally, tax revenues support Singapore’s continued economic growth, enabling the government to invest in innovation, sustainability, and future economic resilience. With a transparent and efficient tax collection system, IRAS ensures that Singapore remains an attractive and stable environment for businesses and investors.
How Does IRAS Manage Tax Collection?
The way IRAS manages tax collection is a key part of Singapore’s reputation as a global business hub. By maintaining an efficient and transparent tax administration, IRAS fosters a reliable and predictable tax environment. Businesses can operate with confidence, knowing that Singapore’s tax system is fair, consistent, and aligned with international best practices. This stability attracts global businesses and investors, encouraging them to base their operations in Singapore. Furthermore, the revenue generated by IRAS supports ongoing investments in infrastructure and public services, which in turn strengthens the nation’s competitive edge on the global stage. As a result, IRAS’s tax collection efforts not only fund public services but also contribute to maintaining Singapore’s status as one of the most competitive and innovative economies in the world.
In addition to its core tax functions, IRAS plays a strategic role in shaping tax policy, providing advisory services to the government, and ensuring that Singapore remains compliant with international tax standards. The taxes collected by IRAS are critical not only for sustaining public services but also for maintaining the high standard of living enjoyed by Singapore’s residents. By effectively managing these revenue streams, IRAS helps position Singapore as an attractive destination for businesses, entrepreneurs, and investors from around the globe.
Breakdown of Tax Revenue Collection
The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) plays a crucial role in sustaining the country’s financial stability through its efficient tax collection systems. In the fiscal year 2023/24, Singapore saw a significant increase in tax revenue, driven by strong economic activity and higher consumer spending. The following breakdown provides a detailed overview of the contributions from various tax types to IRAS’s total revenue collection, highlighting the key factors influencing growth in corporate and individual taxes, as well as the impact of consumer behavior and property transactions.

Tax Exemptions and Territorial Taxation
One of the distinguishing features of Singapore’s tax system is its exemption of certain types of income. Unlike many other countries, dividends, capital gains, and inheritance are not subject to taxation in Singapore. This is an attractive feature for both businesses and high-net-worth individuals, as it allows for tax efficiency and wealth preservation. This tax exemption policy enhances Singapore’s position as a global financial center and makes it a favorable jurisdiction for international businesses and investors.
Additionally, Singapore adopts a territorial taxation system, which means that only income sourced within Singapore is subject to tax. If a company or individual generates income outside of Singapore, and that income is not brought into the country, it is generally not taxed by IRAS. This approach encourages businesses to establish operations in Singapore, knowing they will not be taxed on their foreign-earned income. It also facilitates international business and trade by reducing the overall tax burden for companies that operate in multiple jurisdictions.
The Advisory Role of IRAS
In addition to tax collection, IRAS also serves an advisory role in the development and administration of Singapore’s tax policies. It works closely with the Ministry of Finance to craft tax policies and legislation that support the country’s economic goals. This advisory function ensures that Singapore’s tax laws are competitive, fair, and conducive to business growth. It is a key aspect of IRAS’s work, as it helps the government shape policies that attract foreign investment, promote innovation, and ensure long-term economic stability.
One of the most significant aspects of IRAS’s advisory role is its work on Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs). Singapore has signed over 100 DTAs with countries around the world, preventing businesses and individuals from being taxed twice on the same income. These agreements are particularly beneficial for companies with international operations, as they help streamline tax obligations and reduce the tax burden on cross-border income. DTAs are a cornerstone of Singapore’s business-friendly tax regime and are essential for facilitating international trade and investment.
IRAS Filing Calendar 2025
To ensure businesses and individuals meet their tax obligations, IRAS provides a detailed Filing Calendar each year. This calendar outlines key filing deadlines for various taxes, including income tax, GST, and property tax. Adhering to these deadlines is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. The filing calendar helps businesses stay organized and ensures that their tax filings are submitted in a timely manner.
For 2025, some of the key filing deadlines include:
- 31 January: Property Tax Bill for 2025
- 1 March: Employment Income e-Submission
- 31 March: ECI Filing for companies with a December year-end
- 31 May: FATCA and CRS Returns
- 31 October: GST Return for the September period
- 31 December: Corporate Income Tax Returns (Form C-S, Form C-S (Lite))
By staying informed about these important deadlines, businesses can avoid unnecessary fines and ensure their tax matters are handled smoothly.
IRAS’s Digital Integration and Compliance Tools
Business Access
IRAS offers various digital tools to simplify the process of tax filing and compliance for businesses and individuals. The myTax Portal is the central platform for managing tax affairs. Businesses use CorpPass to sign in to the portal, which allows them to submit their tax returns, check their tax status, and manage payments and refunds online. The platform is user-friendly and designed to streamline tax processes, reducing administrative burdens for businesses.

Individual Access
For individuals, SingPass provides secure access to the myTax Portal. The system ensures that personal tax matters are handled confidentially and efficiently. Additionally, IRAS allows businesses to integrate approved accounting software with the myTax Portal, ensuring that data flows seamlessly between financial systems and the tax authority.

Best Practices for IRAS Compliance
To maintain good standing with IRAS and ensure smooth operations, businesses should follow several best practices for compliance:
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keep detailed and organized records of all business transactions, including sales, purchases, and expenses. Accurate record-keeping ensures that your tax returns reflect the true financial position of the company.
- File on Time: Always meet filing deadlines to avoid penalties. Late submissions incur fines, and repeated delays can result in more severe consequences.
- Leverage Digital Tools: Use the myTax Portal and approved accounting software to streamline tax filings and reduce errors.
- Engage Professional Support: Work with corporate service providers like Corpzzy, who specialize in managing tax matters and ensuring compliance with IRAS regulations.
IRAS Digital Assistance: IRAS Bot
For quick guidance and answers to common tax-related questions, businesses and individuals can use the IRAS Bot, an automated virtual assistant available on the IRAS website. The IRAS Bot is a helpful tool for addressing basic queries, allowing users to resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Questions? We Have Answers
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!




